VPN
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a technology that creates a secure, encrypted connection over the internet between your device (like a computer or smartphone) and another network. This connection acts like a private tunnel, making it seem as if you’re directly connected to the network you’re accessing, even if you’re actually far away or using a public Wi-Fi network. VPNs are used to protect online privacy, secure data, and access restricted or blocked content.
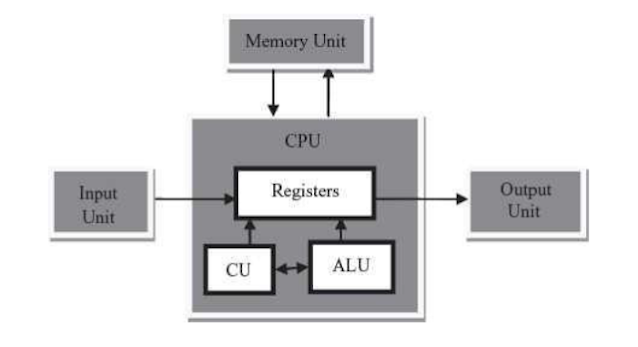
How VPN Works
Imagine you’re in a crowded café using their free Wi-Fi. Without a VPN, any data you send or receive, like browsing or sending emails, is open for others on the same network to intercept. A VPN hides this data by encrypting it—making it unreadable to anyone who doesn’t have the key to decrypt it.
How VPNs Work:2.Encryption:
All internet traffic is encrypted before it is sent to the VPN server.
3. Rerouting:
The encrypted data is routed through the VPN server, which then sends it to the destination.
4. Decryption and Transmission:
Why Use a VPN?
- Enhanced Privacy: Hides your IP address and browsing data from trackers and hackers.
- Increased Security help protect your data from eavesdropping and cyber threats while on public Wi-Fi network
- Accessing Restricted Content: VPNs can allow access to content restricted by region, like certain websites or streaming services.
- Security on Public Wi-Fi: Protects your data from being intercepted when using open networks.
- Remote Work and Secure Access: Allows employees to securely access their company’s network remotely.
Types of VPNs
- Remote Access VPN: The most common type used by individuals and businesses to access a network remotely.
- Site-to-Site VPN: Often used by businesses to connect two networks securely over the internet.
- Personal VPN Services: VPN providers like NordVPN, ExpressVPN, and others offer user-friendly apps to secure individual devices.
- Cloud VPN: Provides a secure connection between a cloud environment and other networks.
- SSL VPN: Uses SSL/TLS protocols to create a secure connection.
Setting Up and Using a VPN
- Choose a VPN provider (like NordVPN or ExpressVPN) and download their app.
- Create an account and select a subscription plan.
- Open the VPN app, log in, and choose a server location.
- Connect to the VPN server—your internet traffic will now be encrypted.
ExpressVPN, NordVPN, CyberGhost VPN, Surfshark, Proton VPN, and TunnelBear.

Comments
Post a Comment